Malattia e staphylococcus Aureus
Articolo informativo di Giuseppe Pinna per S. O. S. - “Osteomielitici d’Italia” - Onlus «Centro Servizi Informativi On-line per Osteomielitici e Pazienti dell’Ospedale CODIVILLA-PUTTI di Cortina d’Ampezzo.

Guidelines for the Management of Community-Acquired Methicillin .
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) Infections in the US Navy and Marine Corps . community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus . ->

Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying .
Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus . Infections caused by community-acquired (CA)-
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) Infections in the US Navy and Marine Corps . community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus . ->

Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying .
Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus . Infections caused by community-acquired (CA)-

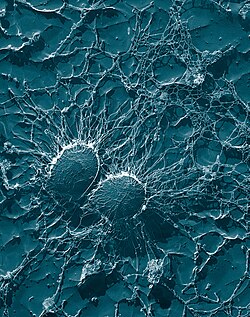
Staphylococcus aureus può verificarsi come un commensale sulla pelle umana; si verifica anche nel naso frequentemente (in circa un terzo della popolazione) e gola meno comunemente. La presenza di 's. aureus ' in queste circostanze non indica sempre infezione e quindi non sempre richiede trattamento (infatti, il trattamento può essere inefficacia e può verificarsi ricolonizzazione). Può sopravvivere su animali domestici come cani, gatti e cavalli e può causare bumblefoot nei polli. Può sopravvivere per qualche ora su superfici dell'ambiente asciutti, ma l'importanza dell'ambiente nella diffusione del 's. aureus ' è attualmente in discussione. Esso può ospitare fagi, come ad esempio il leukocidin di Panton-Valentine, che aumentano la sua virulenza.
' S. aureus ' può infettare altri tessuti quando le barriere sono state violate (ad esempio, pelle o rivestimento mucoso). Questo porta a foruncoli (bolle) e carbonchi (una raccolta di foruncoli). In neonati 's. aureus ' infezione può causare una sindrome di pelle scottate stafilococcica malattia grave (SSS).
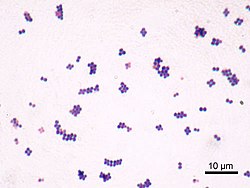
' S. aureus ' alv infezioni possono essere diffuse attraverso il contatto con pus da una ferita infetta, il contatto pelle a pelle con una persona infetta producendo ialuronidasi che distruggono i tessuti e contatto con oggetti come asciugamani, lenzuola, abbigliamento o atletiche attrezzature utilizzate da una persona infetta. Penetrando profondamente ' s. aureus ' infezioni possono essere grave. Articolazioni protesiche mette una persona ad un particolare rischio per artrite settica e stafilococcica endocardite (infezione delle valvole cardiache) e polmonite, che può essere diffuso rapidamente.
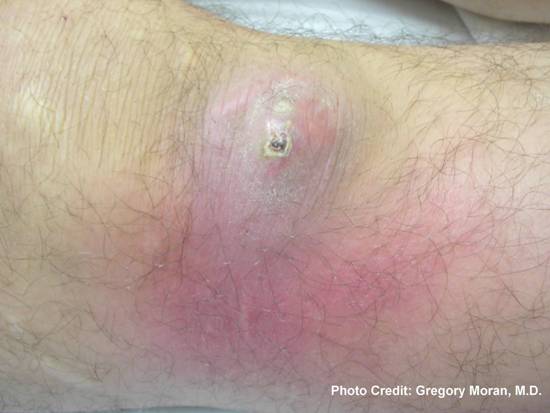
Fotografia raffigurato un ascesso cutaneo, che era stato causato da batteri meticillino-resistenti Staphylococcus aureus, cui si riferisce l'acronimo MRSA. Photo credit: Gregory Moran, M.D.
Dermatite atopica
' S. aureus ' è estremamente diffusa in pazienti di dermatite atopica, che sono meno resistenti ad esso rispetto alle altre persone. Esso provoca spesso complicazioni. La malattia è più probabile trovare in fertile attivi posti compreso, le ascelle, capelli e cuoio capelluto. I grandi brufoli che appaiono in quelle zone possono causare il peggiore dell'infezione se spuntato. Questo può portare alla sindrome di pelle Scalded. Una grave forma di questo è malattia Ritter visto nei neonati.
Sindrome da shock tossico e intossicazione alimentare ' s. aureus '
Alcuni ceppi di 's. aureus ', che producono esotossina TSST-1, sono gli agenti causali di sindrome da shock tossico. Alcuni ceppi di 's. aureus ' anche producono un enterotossina che è l'agente scatenante di gastroenterite ' s. aureus '. La gastroenterite è autolimitante con la persona sempre meglio in 8–24 ore. I sintomi comprendono nausea, vomito, diarrea e dolori addominali.

Mastite nelle vacche
' S. aureus ' è uno degli agenti causali di mastiti nelle vacche da latte. Sua grande capsula protegge l'organismo dall'attacco di difese immunologiche di mucca. e la morte.
Ulteriore lettura
- Che cosa è Staphylococcus Aureus?
- Staphylococcus Aureus microbiologia
- Fattori di virulenza Staphylococcus Aureus
- Staphylococcus Aureus diagnosi
- Staphylococcus Aureus trattamento
- Staphylococcus Aureus prevenzione



staphylococcus aureus infection









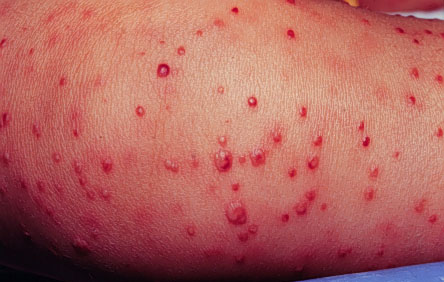


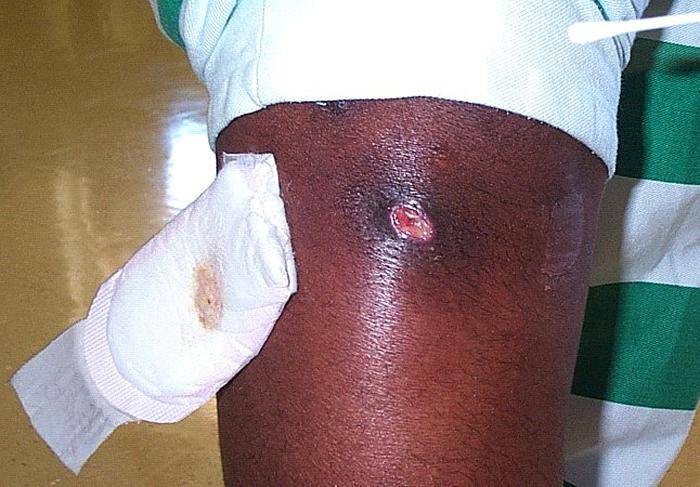
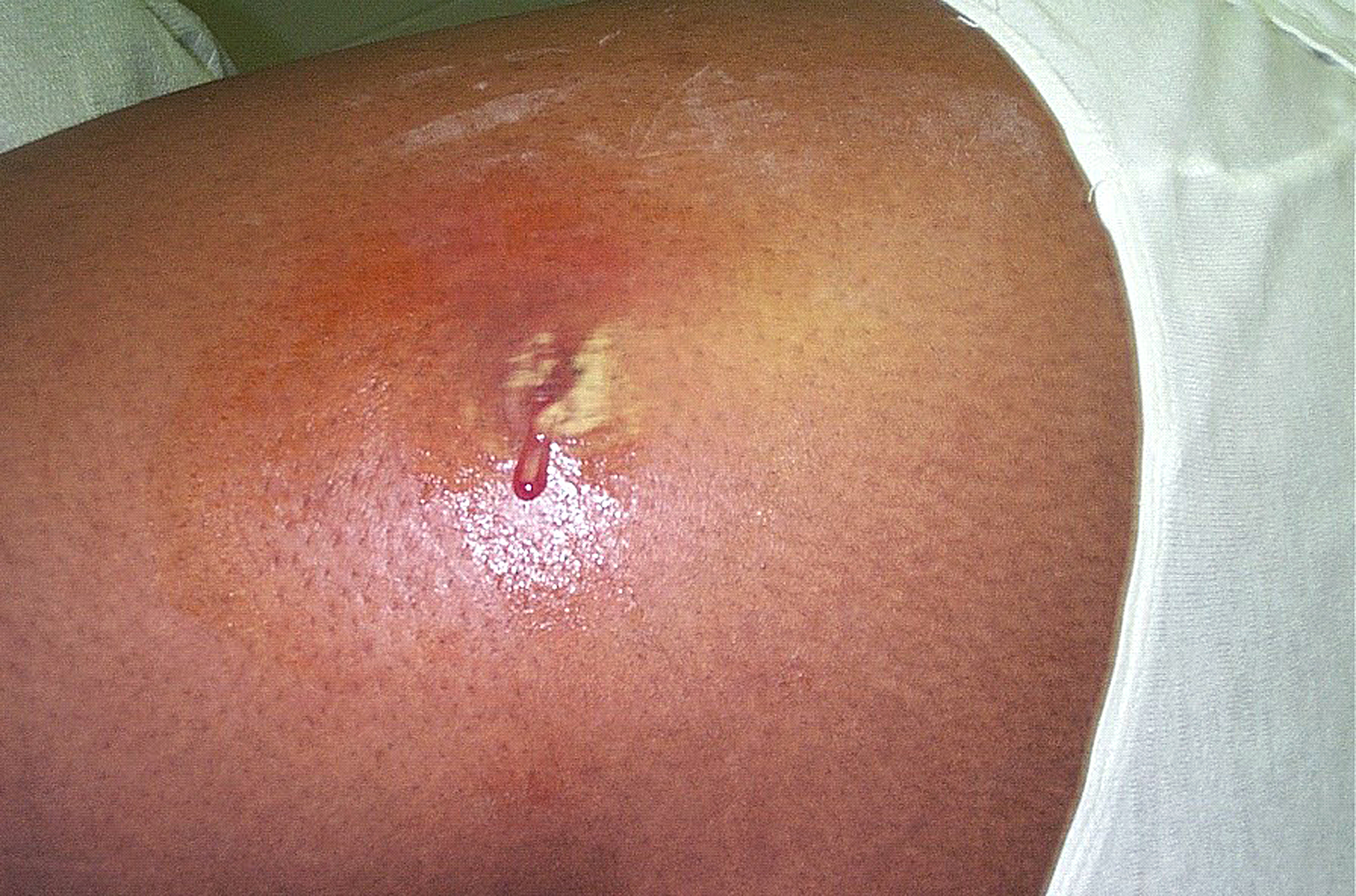



Figure 1
Anatomy of cutaneous immune responses. ↓

Figure 2
Major host cell signalling pathways involved in the immune response against S. aureus cutaneous infections. ↓

Figure 3
Mechanisms of IL-1α and IL-1β production during S. aureus cutaneous infections. ↓

Figure 4
The IL-1-mediated cutaneous immune response against S. aureus. ↓
Figure 5
The IL-17-mediated cutaneous immune response against S. aureus. ↓
Figure 6
Potential immunomodulatory and vaccination strategies that might help to promote immunity and provide a therapeutic advantage against cutaneous S. aureus infections. ↓
Table 1
Human neutrophil and T cell defects associated with Staphylococcus aureus skin infections ↓| Immune defect | Diseases |
|---|---|
| Neutrophils | |
| Neutropenia | Severe congenital neutropenia and neutropenic patients (such as patients undergoing chemotherapy) |
| Defective oxidative burst | Chronic granulomatous disease, myeloperoxidase deficiency and G6PD deficiency |
| Defective chemotaxis | Leukocyte adhesion deficiency type I, Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome and RAC2 deficiency |
| Granule disorders | Neutrophil-specific granule deficiency and Chediak–Higashi syndrome |
| Combined defects in oxidative burst, chemotaxis and phagocytosis | Diabetes mellitus and renal insufficiency (in particular, patients on haemodialysis) |
| Signalling | |
| Defects in IL-1R or TLR signalling | MYD88 deficiency and IRAK4 deficiency |
| T cells | |
| Decreased TH17 cell numbers | Hyper-IgE syndrome (caused by STAT3 and DOCK8 mutations that render patients deficient of TH17 cells) |
| Atopic dermatitis (caused by skin barrier defects, including filaggrin mutations, that lead to decreased levels of antimicrobial peptides, increased TH2 cell responses and decreased TH17 cell responses) | |
| HIV/AIDS (which results in decreased numbers of CD4+ T cells, including TH17 cells) | |
| IL-17F and IL-17RA deficiency (or patients with autoantibodies specific for IL-17A, IL-17F and IL-22) | Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis (in which patients have increased susceptibility mainly to mucocutaneous Candida infections, but also to S. aureus skin infections) |
| DOCK8, dedicator of cytokinesis 8; G6PD, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; IL, interleukin; IL-1R, IL-1 receptor; IL-17RA, IL-17 receptor A; IRAK4, IL-1R-associated kinase 4; MYD88, myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TH, T helper; TLR, Toll-like receptor. | |
Molecular Mechanisms of Staphylococcus aureus ↓

Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus.
 Staphylococcus aureus and granulocytopenia
Staphylococcus aureus and granulocytopenia
Pediatric AIDS Pictoral Atlas, Baylor International Pediatric AIDS Initiative
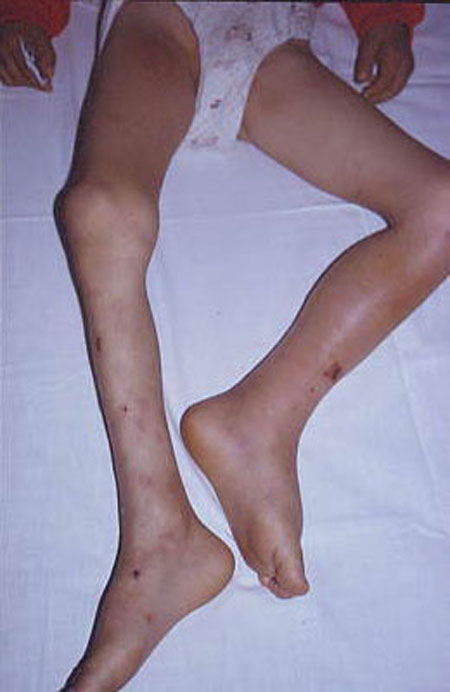

Staphylococcus aureus
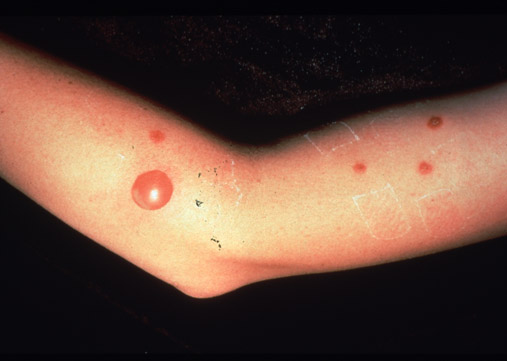

Staphyolococcus aureus may cause furuncles (boils). ↓
_.jpg)


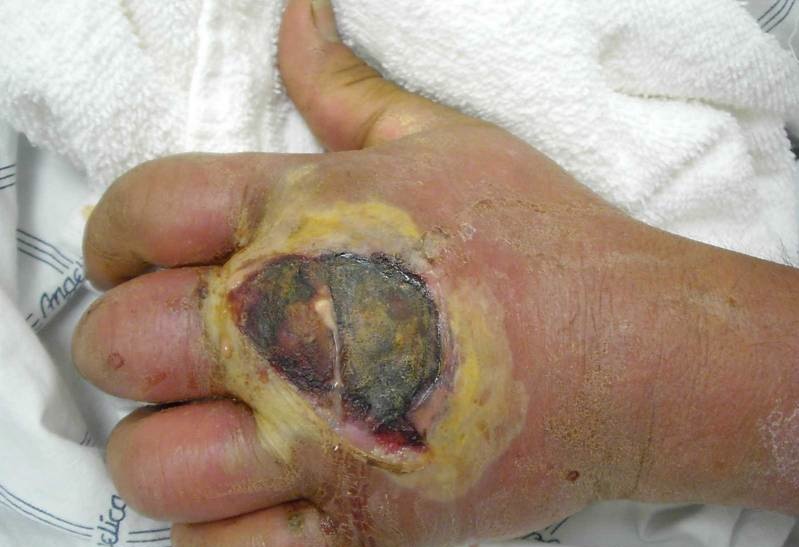
Infection of the hand caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Photo Credit: Gregory Moran, M.D., from the Center for Disease Control and Prevention ↓


Fine
Pubblicato su Blogger oggi 26 Agsto 2012 alle ore 13,55 da: Giuseppe Pinna de Marrubiu




Nessun commento:
Posta un commento